面试题如下
@interface DXPerson : NSObject
@property (copy, nonatomic) NSString *name;
- (void)print;
@end
// ----------分割线----------
@implementation DXPerson
- (void)print{
NSLog(@"my name is %@", self->_name);
}
@end
1.编译能否通过? 2.如果能通过,打印结果是什么?
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [DXPerson class];
void *obj = &cls;
[(__bridge id)obj print];
打印结果
my name is <ViewController: 0x7f8ba1f1a300>
复习以前的知识
对象的isa指针指向哪里?
- instance对象的isa指向class对象
- class对象的isa指向meta-class对象
- meta-class对象的isa指向基类的meta-class对象
Objective-C对象的本质
@interface Student : NSObject{
int _no;
int _age;
}
struct Student_IMPL {
struct NSObject_IMPL NSObject_IVARS;
int _no;
int _age;
}
struct NSObject_IMPL {
Class isa;
}
因此归根结底:
struct Student_IMPL {
Class isa;
int _no;
int _age;
}
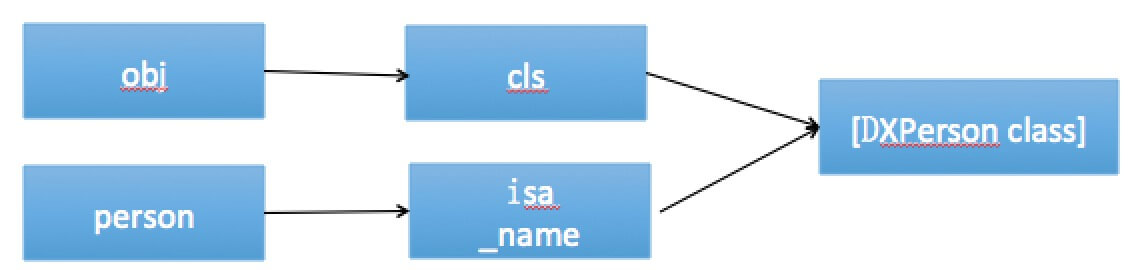
根据这张图,我们就明白了为什么可以通过编译,并且可以调用成功,本质上都是找到类对象,然后调用对象方法.
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSString *test = @"123";
id cls = [DXPerson class];
void *obj = &cls;
[(__bridge id)obj print];
}
发现name打印竟然是123
my name is 123
为什么如此神奇呢??
局部变量分配在栈空间
栈空间分配,是连续的,从高地址到低地址
void test(){
// 8个字节
long long a = 4; // 0x7ffee638bff8
long long b = 5; // 0x7ffee638bff0
long long c = 6; // 0x7ffee638bfe8
long long d = 7; // 0x7ffee638bfe0
NSLog(@"%p %p %p %p", &a, &b, &c, &d);
}
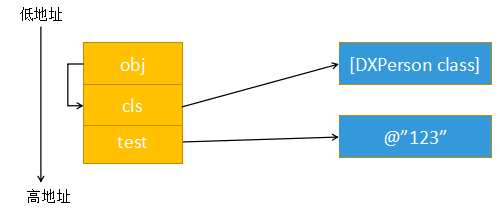
struct DXPerson_IMPL{
Class isa;
NSString *_name;
};
如图cls相当于isa,他们所在的栈空间地址是连续的,查找_name,是根据DXPerson的结构体查找,从第8个字节开始查找,于是就找到了test